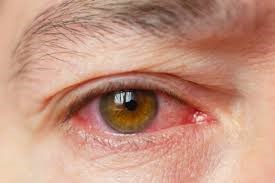
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis refers to inflammation of the thin, translucent tissue (conjunctiva) that lines the white part of the eye.
It usually refers to red eye – an infection of the conjunctiva due to a virus, or less commonly, due to bacteria. This is typically an acute infection associated with flu-like symptoms and is extremely contagious. Fortunately, viral conjunctivitis will commonly recover on its own, although this may take anywhere from one to three weeks.
Other causes of conjunctivitis are:
- Allergic conjunctivitis – patients may have underlying allergic disease such as eczema, asthma and allergic rhinitis etc .
- Blepharitis – due to excessive secretions and inflammation of the eye lids.
Conjunctivitis - Symptoms
- Redness of one / both eyes
- Eye discharge – watery or stringy discharge and sticky eyes in the mornings
- Itchiness and discomfort
- Eyelid swelling
- May have a mild fever, sore throat or runny nose
Conjunctivitis - Prevention
- Wash your hands before and after touching your eyes or face. The virus may be on your hands, and may then spread to other family and friends when they touch the same surfaces that you have touched
- Avoid touching of shared surfaces – such as table tops, door knobs and telephones
- Do not share towels, linen, pillows and bedsheets
- Do not share eye drops
- Take time off from school or work until the eyes are no longer red, to avoid spreading to classmates and colleagues
Conjunctivitis - Treatments
Treatment is usually symptomatic. Antibiotic eye drops may sometimes be prescribed if bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected with pussy discharge
Disclaimer – Above are just general information and patients are advised to see their Eye Doctors for professional treatment.
